Reveal Cards In Increasing Order - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
정수 카드 목록 list가 주어진다.
이 list를 랜덤 하게 섞은 뒤, 아래 순서대로 카드를 뽑았을 때 카드를 뽑는 순서가 오름차순이 되게 하는 섞인 list를 반환하는 문제다.
뽑는 방법은 아래와 같다.
- 맨 앞의 카드를 뽑는다.
- 그다음 카드를 맨 뒤로 돌린다.
예시
Input: deck = [17,13,11,2,3,5,7]
Output: [2,13,3,11,5,17,7]
Explanation:
We get the deck in the order [17,13,11,2,3,5,7] (this order does not matter), and reorder it.
After reordering, the deck starts as [2,13,3,11,5,17,7], where 2 is the top of the deck.
We reveal 2, and move 13 to the bottom. The deck is now [3,11,5,17,7,13].
We reveal 3, and move 11 to the bottom. The deck is now [5,17,7,13,11].
We reveal 5, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [7,13,11,17].
We reveal 7, and move 13 to the bottom. The deck is now [11,17,13].
We reveal 11, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [13,17].
We reveal 13, and move 17 to the bottom. The deck is now [17].
We reveal 17.
Since all the cards revealed are in increasing order, the answer is correct.1. 순열 완전 탐색
from collections import deque
from itertools import permutations
from typing import *
class Solution:
def deckRevealedIncreasing(self, deck: List[int]) -> List[int]:
target = sorted(deck)
for item in permutations(deck, len(deck)):
temp = []
q = deque(item)
while q:
temp.append(q.popleft())
if q:
q.append(q.popleft())
if temp == target:
return list(item)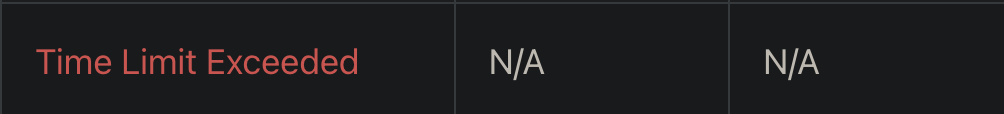
섞을 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 구해서 조건에 맞게 시뮬레이션하고 맞으면 반환한다.
TLE 났다.
2. 순열 완전 탐색 최적화
from collections import deque
from itertools import permutations
from typing import *
class Solution:
def deckRevealedIncreasing(self, deck: List[int]) -> List[int]:
target = sorted(deck)
if len(target) % 2 != 0:
target2 = target[:(len(deck) // 2) + 1]
target3 = target[(len(deck) // 2) + 1:]
else:
target2 = target[:(len(deck) // 2)]
target3 = target[(len(deck) // 2):]
for item in permutations(target3, len(target3)):
# print(item)
temp, temp2, temp3 = [], deque(target2[:]), deque(list(item))
while temp2 or temp3:
if temp2:
temp.append(temp2.popleft())
if temp3:
temp.append(temp3.popleft())
# print(temp)
q = deque(temp)
temp4 = []
while q:
temp4.append(q.popleft())
if q:
q.append(q.popleft())
if temp4 == target:
return temp
1번 풀이를 최적화했다.
예를 들어서 [ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9]를 위 조건대로 오름차순으로 뽑으려면 [1, X, 3, X, 5]의 형태를 가진 순열이어야 한다.
그러니깐 X에 해당하는 부분만 순열로 모두 구해서 두 list를 겹쳐서 합친 뒤에 시뮬레이션했다.
여전히 TLE가 났다.
3. index를 이용한 풀이
from typing import *
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def deckRevealedIncreasing(self, deck: List[int]) -> List[int]:
sorted_deck = sorted(deck)
answer = [0] * len(sorted_deck)
q = deque([i for i in range(len(sorted_deck))])
for i in range(len(sorted_deck)):
print(f"q: {q}, answer: {answer}")
answer[q.popleft()] = sorted_deck[i]
if q:
q.append(q.popleft())
return answer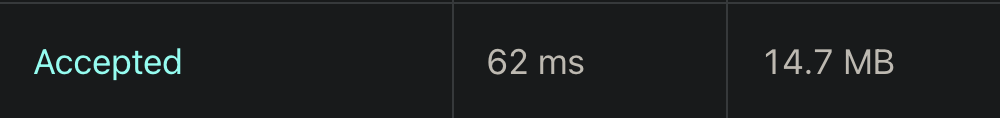
오름차순 정렬된 list를 가지고 시뮬레이션하면 원하는 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
정확히는 오름차순 정렬된 list의 index를 queue에 넣고 queue를 시뮬레이션하면서 queue에서 빠져나온 인덱스 값에 해당하는 값을 answer 배열에 할당해주면 된다.
시뮬레이션하면 다음과 같다.
q: deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]), answer: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
q: deque([2, 3, 4, 1]), answer: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0]
q: deque([4, 1, 3]), answer: [1, 0, 3, 0, 0]
q: deque([3, 1]), answer: [1, 0, 3, 0, 5]
q: deque([1]), answer: [1, 0, 3, 7, 5]
[1, 9, 3, 7, 5]
답으로 얻어야 하는 배열에서 오름차순 순서대로 0, 2, 4.... 번 인덱스부터 값을 채워 넣어야 하는 규칙 말곤 찾지 못했고, 무엇보다 동일한 규칙으로 섞인 배열과 정렬된 배열을 왔다 갔다 하는 것이 불가능하다고 생각해서 완전 탐색으로 삽질한 문제.
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 95. Unique Binary Search Trees II (0) | 2021.08.29 |
|---|---|
| 1079. Letter Tile Possibilities (0) | 2021.08.29 |
| 1557. Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes (0) | 2021.08.25 |
| 1561. Maximum Number of Coins You Can Get (0) | 2021.08.24 |
| 1382. Balance a Binary Search Tree (0) | 2021.08.23 |