Sort List - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
단방향 연결 리스트가 주어진다.
주어진 연결 리스트를 value 값 기준으로 오름차순 정렬해 반환하는 문제다.
단 가능하다면 시간 복잡도를 O(NlogN), 추가 공간 없이 해결해보는 것이 요구사항이다.
예시

Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]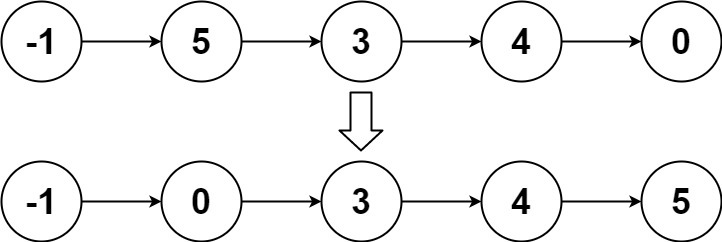
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]풀이 1
from typing import *
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
trace = []
cur = head
while cur:
trace.append(cur)
cur = cur.next
trace.sort(key=lambda x: x.val)
for i in range(1, len(trace)):
trace[i - 1].next = trace[i]
trace[-1].next = None
return trace[0]
시간 복잡도는 O(N) + O(NlogN) + O(N) = O(NlogN), 공간 복잡도는 N인 풀이법이다.
가장 단순하게 연결 리스트를 탐색하면서 노드를 trace에 저장하고 trace를 value 기준으로 정렬한 뒤 앞에서 뒤로 차례대로 연결해주면 해결할 수 있다.
풀이 2
from typing import *
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
p1, p2 = head, head.next
while p2 and p2.next:
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next.next
right = p1.next
p1.next = None
left = head
left_sorted_list = self.sortList(left)
right_sorted_list = self.sortList(right)
return self.merge(left_sorted_list, right_sorted_list)
def merge(self, left, right):
if not left:
return right
if not right:
return left
temp = ListNode(0)
cur = temp
while left and right:
if left.val >= right.val:
cur.next = right
right = right.next
else:
cur.next = left
left = left.next
cur = cur.next
cur.next = left if left else right
return temp.next
시간 복잡도는 O(N) * O(logN) = O(NlogN), 공간 복잡도는 logN인 풀이다. Top-Down 방식으로 머지 소트를 구현하는 방식이다. 시간 복잡도는 O(N)이 두 연결 리스트의 head의 value를 비교하면서 병합하기 때문에 걸리는 시간이고, O(logN)이 머지 소트의 최대 깊이(ㅇepth)이기 때문에 둘을 곱한 값이 총 시간 복잡도가 된다.
공간 복잡도의 경우 최대 깊이만큼 재귀 call stack에서 추가 메모리를 저장하기 때문에 logN 만큼의 공간을 소모한다.
머지 소트의 top-bottom 구현 방식이다.
풀이 3
class Solution(object):
def sortList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head or not head.next: return head
def getSize(head):
# Simply count the length of linked list
counter = 0
while head:
counter +=1
head = head.next
return counter
def split(head, size):
# given the head & size, return the the start node of next chunk
for i in range(size-1):
if not head:
break
head = head.next
if not head: return None
next_start, head.next = head.next, None #disconnect
return next_start
def merge(l1, l2, dummy_start):
# Given dummy_start, merge two lists, and return the tail of merged list
curr = dummy_start
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
curr.next, l1 = l1, l1.next
else:
curr.next, l2 = l2, l2.next
curr = curr.next
curr.next = l1 if l1 else l2
while curr.next: curr = curr.next # Find tail
# the returned tail should be the "dummy_start" node of next chunk
return curr
total_length = getSize(head)
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
start, dummy_start, size = None, None, 1
while size < total_length:
dummy_start = dummy
start = dummy.next
while start:
left = start
right = split(left, size) # start from left, cut with size=size
start = split(right, size) # start from right, cut with size=size
dummy_start = merge(left, right, dummy_start) # returned tail = next dummy_start
size *= 2
return dummy.next
풀이 2와 동일하게 머지 소트를 구현했으나 bottom-up 방식이다.
시간 복잡도는 O(N) * O(logN) = O(NlogN), 추가 공간을 사용하지 않는 문제의 정해다.
즉 이 문제는 머지 소트를 bottom-up 방식으로 구현하라는 문제다.
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 16. 3Sum Closest (0) | 2021.11.02 |
|---|---|
| 41. First Missing Positive (0) | 2021.11.01 |
| 329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix (0) | 2021.10.28 |
| 295. Find Median from Data Stream (0) | 2021.10.27 |
| 42. Trapping Rain Water (0) | 2021.10.26 |